Imagine yourself sitting at your computer, browsing, playing games, and staying connected with friends. The computer helping with all these tasks is what we call a digital computer. But have you ever heard of Hybrid computers? Today, in this article we’re going to discuss what is hybrid computer, example of hybrid computer, its types, advantages and disadvantages.
See here’s the thing, for how amazing our digital computer is, there are some very difficult problems that they can’t do, like handling complex mathematical problems, complicated scientific events, etc. This is what we need Analog computers for.
Now what if we combine the strength of these two computers? Interesting right! An innovative mix of both digital and analog computing power is what we call a hybrid computer. But what is Hybrid computer? What are the examples of Hybrid computer. Let’s dive into it.
what is hybrid computer
Hybrid Computer Definition – A Hybrid computer is a type of computer that combines the features and functions of both analog and digital computers. They are designed to perform complex calculations and handle challenging scientific phenomena which is not possible by a regular computer.
Vannevar Bush, an American engineer, inventor, and science administrator laid the foundation for combining analog and digital elements in computing systems. Packard Bell, a Dutch-based computer manufacturing company, designed the first Hybrid computer in 1961 called Hycomp 250.
The Analog component of the Hybrid computer performs tasks that require instant data processing and control, whereas the Digital component is responsible for doing complex calculations and difficult algorithms with high precision and accuracy.
You May Also Like :
We can find the applications of Hybrid computers in various fields, such as Aerospace applications, Financial Modeling, Robotics, Weather Forecasting, Data Analytics, etc. They are also used by many big organizations like NASA and Boeing for Radar and signal processing, trajectory calculations, etc.
types of hybrid computer
There are 3 types of Hybrid computer –
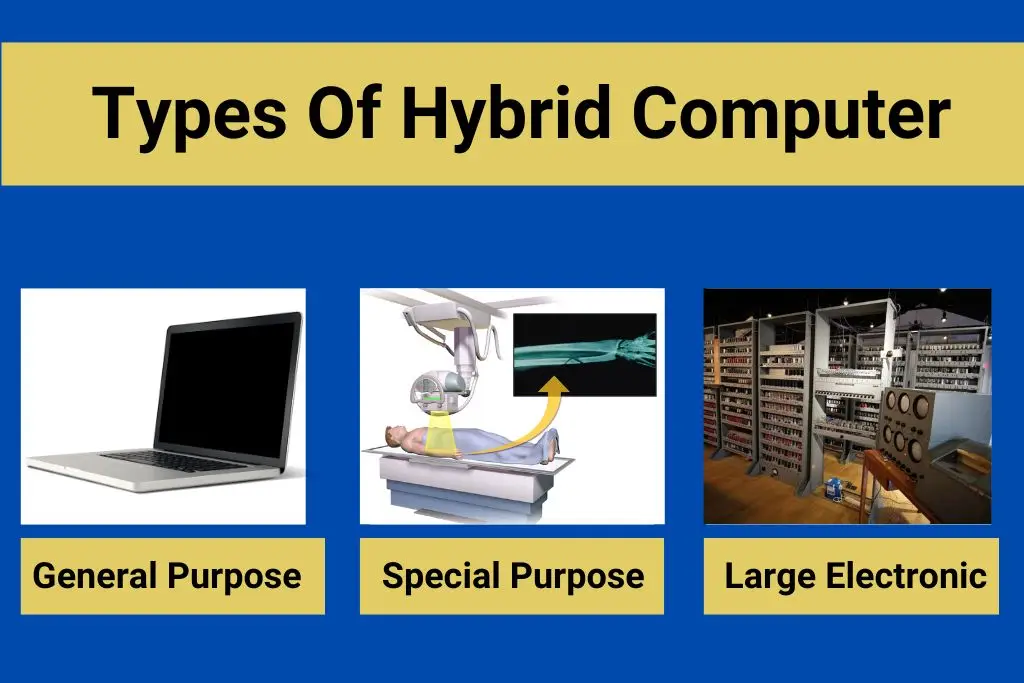
Large Electronic Hybrid Computer
The Large Electronic Hybrid Computers is one of the types of Hybrid computer that were designed and developed in 1950-1960. They were made using numerous hundreds of amplifiers. The amplifiers are used in different arrangements such as operational amplifiers, differential amplifiers, and specialized amplifiers based on the requirements of the exact application.
As they have hybrid design these computers are able to solve complex equations involving continuous variables, nonlinear equations, etc.
Examples – These types of hybrid computer are used in Astrophysics, Astronomy, Medical research, Oil and Gas Industry, Chemical Kinetics, etc.
General-Purpose Hybrid Computers
General-Purpose Hybrid Computers are the type of Hybrid computer that can solve many issues, handle various tasks smoothly all at the same time with a higher speed. These computers are flexible, fast, and suitable for applications like simulations, control systems, optimization, and real-time tasks.
Example – These types of hybrid computer include scientific research, Advanced Signal Processing, Artificial Intelligence, Robotics and Automation, etc.
Special-Purpose Hybrid Computers
As suggested by the name, Special-Purpose Hybrid Computers are those types of hybrid computer that were designed to address particular tasks or applications. They have a fixed program to handle a specific problem. They are required in places where extreme supervision is needed like hospitals, fire stations, forensic labs, etc.
These types of hybrid computer can be embedded into physical systems such as subsystem simulators, results analyzers, or function controllers to enhance the performance.
Example – used in Cryptography and Security, encoding data, Signal and Image Processing, square-root operations on input signals, etc.
Other than these, there are other types of Hybrid computer as well such as Hybrid Supercomputers, Hybrid Control Systems for robotics, Hybrid Neural Networks for artificial intelligence and machine learning, and Mixed-Signal Integrated Circuits used in microelectronics for communication systems.
hybrid computer images

examples of hybrid computer
Hybrid computers are used in many applications and fields. We can see the example of Hybrid computers in many aspects of our lives. Some of the examples of Hybrid computer are –
Smartphones – it is one of the most common examples of Hybrid computer. It uses analog-to-digital converters for audio processing or touch screen controllers.
Digital Cameras – many digital cameras use hybrid systems and are examples of hybrid computer for image stabilization.
Audio Equipment – some high quality audio equipment uses hybrid amplifiers to provide efficient sound production.
Health Monitoring Devices – some medical devices, like electrocardiograms (ECGs), echocardiogram machines, ultrasound machines, or health trackers are some very important examples of hybrid computer, may have analog sensors to measure physiological signals.
Power Management – electronic devices, such as power inverters and converters, may employ hybrid systems to efficiently manage power conversion.
Weather Forecasting – Other examples of hybrid computer include weather forecasting. Hybrid computers are used to model complex weather patterns to predict weather conditions accurately.
Flight Simulators – to provide realistic training for pilots.
Nuclear Reactor Control – In nuclear power plants, hybrid computers are used to monitor and control reactor systems.
Aerospace Guidance Systems – In spacecraft and missiles, hybrid computers play a vital role in guidance and control systems.
Robotics – used to control complex movements and tasks.
Home Appliances – appliances such as washing machines and air conditioners are also examples of hybrid computer. They use hybrid technology for efficient control and monitoring.
Gaming Consoles – gaming consoles incorporate hybrid computing elements, such as analog joysticks and buttons with powerful digital processors for graphics and game logic.
GPS Navigation Systems – GPS devices use a mix of analog radio signals from satellites and digital processors to calculate accurate positioning and provide navigation guidance.
Home Security Systems – home security systems are also examples of hybrid computer, where analog sensors detect motion, door/window openings, and trigger alarms or notifications.
ATM Machines – ATMs may use hybrid input devices, such as a combination of digital touch screens to select options and numeric keypads for entering PINs and other information.
Electronic Power Steering – In some vehicles, electronic power steering system is a hybrid computer example which uses analog sensors to measure driver input and digital controllers to adjust steering assistance.
Microwave Ovens – for generating microwaves, and for precise time and power settings.
Petrol pumps – for fuel quality testing.
Industrial Automation – In manufacturing and industrial settings, many examples of hybrid computer can be seen where hybrid control systems are commonly used for precise automation.
Adaptive Optics – Some astronomical telescopes use adaptive optics systems that combine analog wave front sensors with digital controllers for clearer astronomical observations.
Mixed-Reality Devices – Devices that enable mixed reality experiences, such as Microsoft HoloLens, are examples of hybrid computer which use hybrid technology to blend real-world visuals with digital overlays for augmented reality interactions.
Biometric Authentication Devices – they use hybrid technology, for capturing biometric data like fingerprint scanners and matching the biometric information.
Electronic Control Units (ECUs) in Vehicles – Modern automobiles are examples of hybrid computer which employ many ECUs to control various functions like engine performance, emissions, and safety systems.
Virtual Instruments – Certain virtual instruments in laboratories combine analog sensors and transducers with digital interfaces to provide real-time data measurements and analysis.
Smart Grid Technology – Another hybrid computer example where hybrid computing is applied in smart grid systems to optimize power distribution and management for improved efficiency.
Internet of Things (IoT) – IoT networks are examples of hybrid computer which often integrate hybrid technology, to transmit the information for monitoring and control.
Traffic Control Systems – Advanced traffic control systems can employ hybrid computing principles, to optimize traffic flow and reduce crowding.
Electronic Voting Systems – It employs hybrid technology, for secure ballot counting and storage.
Ships – Ships are also examples of hybrid computer where hybrid computing principles can be applied in various systems and operations on ships, enhancing efficiency, safety, and performance.
Satellite Communication – employ hybrid technology, this hybrid computer example use radio frequency transmissions for communication between the satellite and ground stations.
So now that we have seen various examples of hybrid computer, let’s move on to the advantages of hybrid computer.
Advantages of Hybrid Computer
As we have seen various Hybrid computer uses above, let’s have a look at the advantages of hybrid computer now. Since, Hybrid computer uses a combination of analog and digital technologies, it offers different advantages such as –
It performs on-line data processing.
Versatility, Hybrid computers are versatile and can handle a wide range of tasks easily due to the flexibility provided by the combination of analog and digital components.
Improved Performance, one of the main advantages of hybrid computer is that they can achieve higher performance levels compared to using only one type of technology. This advantage is particularly relevant in tasks that require real-time responsiveness.
Energy Efficiency, is also one of the important advantages of hybrid computer. They can be designed to optimize energy consumption. Analog components can be used for tasks that require less power, while digital processors can handle more numerical based operations, leading to overall energy efficiency.
Precision and Accuracy, provide high precision and accuracy in complex calculations and simulations. They are among the important advantages of hybrid computer.
Cost-Effectiveness, other advantages of hybrid computer include cost-effectiveness. It provide a cost-effective solution and balance performance.
Flexibility, advantages of hybrid computer includes flexibility as well. Hybrid computer are flexible allowing for the addition or modification of components based on application needs.
Customizable, can be modified to suit specific application requirements for the targeted tasks. It is among the unique advantages of hybrid computer which is very efficient.
After seeing the advantages of hybrid computer, let’s have a look on hybrid computer disadvantages.
Disadvantages of Hybrid Computer
While Hybrid computers offer many advantages, they also have few disadvantages to consider –
Cost, hybrid computer disadvantages include cost. They can be costlier than digital computers as they require expensive circuits, cables and whole set up.
Complexity, it is one of the main hybrid computer disadvantages. The design and implementation of hybrid computers is complex, leading to higher development and maintenance costs.
Maintenance Complexity, maintenance also comes under hybrid computer disadvantages. It can be more challenging due to the need to identify issues in both analog and digital areas.
Power Consumption, other hybrid computer disadvantages include power usage. Some hybrid systems may consume more power than digital computers, especially if both analog and digital components need to function together.
difference between analog digital and hybrid computer
Analog Digital and Hybrid computer are types of computing systems, each with its unique characteristics and applications. The key difference between analog digital and hybrid computer are –
Analog Computer
- Measurement unit is physical values, like temperature, time, and pressure.
- Relatively simple in design and operation, making them easier to construct and understand.
- Processes data in a continuous manner.
- Well-suited for real-time simulations, control systems, and tasks involving continuous mathematical operations.
- Its signal is characterized by Electromagnetic waves.
- They have slow speed.
- Unlike digital computers, analog computers might struggle with tasks that demand Boolean logic operations.
- Analog computers are fit for tasks that need interaction with the physical world because they easily communicate with physical sensors and controllers.
- There are no input and output devices.
- Its components are operational amplifiers, resistors, capacitors, voltage sources and relays.
- More resilient to certain types of noise and interference.
- Require fewer components and do not rely on expensive digital processors.
- Lack the ability to store and retrieve data as efficiently as digital computers.
- Applications – Speed Measurement, Fluid Flow Control, Aircraft Navigation, Vibration Analysis, etc.
- Examples – Thermometers, Analog Clocks, Speedometer, Compasses, etc.
Digital Computer
- It operates on discrete data represented in binary form “0” and “1” .
- The primary measurement unit used for digital computers is binary digits.
- They are more complex in design and operation due to their discrete binary nature.
- Processes data on discrete signals.
- Suitable for general computing, complex calculations, data storage, and multitasking.
- Its signal is characterized by Voltage pulses.
- Comparatively faster than Analog computers.
- Works on the principles of Boolean logic, which is a fundamental part of their operation.
- Digital computers interact with the physical world through digital interfaces through sensors, and controllers.
- There is presence of input and output devices.
- Its main components are input-output devices, main memory, control unit, and arithmetic-logic unit.
- Due to discrete binary signals, they are more resilient to signal interference and noise compared to analog computers.
- Digital computers typically require more components due to their complex architecture and the need for expensive digital processors.
- Can store huge amounts of data in memory units, enabling duplicate results for the same inputs.
- Applications – General-Purpose Computing, Scientific Research, Business and Finance, Entertainment and Gaming, Education, etc.
- Examples – Smartphones, Personal Computers like Dell, HP, IDM, etc. laptops, Servers, GPS Devices, etc.
Hybrid Computer
- Main components are Analog and Digital components.
- It allows for the simultaneous processing of continuous and discrete data due to both Analog and Digital elements.
- The measurement unit depends on the specific application and the nature of the data being processed.
- Can be more complex than analog computers but less complex than digital computers.
- Suitable for tasks that involve real-time interactions with the physical world, continuous data processing, and complex digital calculations.
- Hybrid computers process both analog and digital signals.
- The speed depends on the task and the efficiency of combining analog and digital functionalities.
- Presence of input/output devices.
- Can achieve high accuracy in both continuous and discrete operations.
- It reduces the impact of noise in continuous data processing.
Conclusion
Hybrid computers are powerful computing systems that combine the advantages of both analog and digital technologies. The ability to process both continuous analog data and discrete digital data at once makes them suitable for tasks that demand the strengths of both signal types. Different examples of hybrid computers continue to play an important role in advancing technology and meeting the diverse computing needs of specialized industries showing their value in modern computing applications.
Also Read :
FAQs
What are hybrid computers examples?
- Digital-Analog Hybrid Computer
- Hybrid Supercomputer
- Hybrid Neural Network Computers
What is a hybrid computer short answer?
A hybrid computer is a type of computer that combines the features of both analog and digital computers.
What are characteristics of hybrid computer?
Three characteristics of hybrid computer are:
- Special Purpose Computer
- Real-time Processing
- Data Accuracy
Is ATM a hybrid computer?
No, an ATM (Automated Teller Machine) is not a hybrid computer. Customers can only do simple financial transactions using ATMs, which are automated banking devices, without the help of a human.
Who invented hybrid computer?
Packard Bell in 1961 released first dekstop hybrid computer.
Why is it called a hybrid computer?
It is special computer that have the functionalities of both digital and an analog computer.
What are the disadvantages of hybrid computers?
Hybrid Computer is very costly and it is not available for everyone.