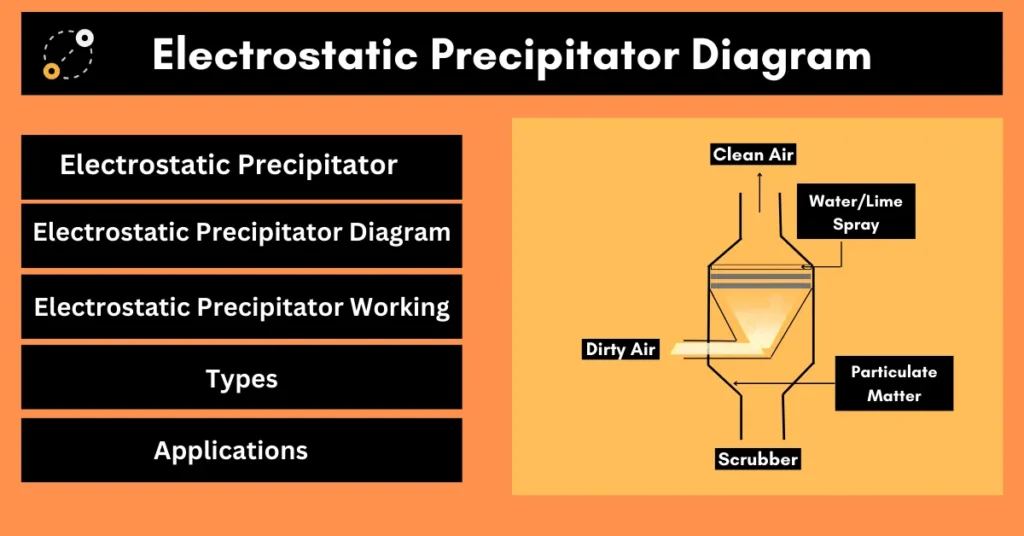
The late 1950s and early 1960s saw great developments that completely changed the computer industry. The second generation of computer represents a crucial stage as computers evolved from large, heat-producing devices to thinner, better-performing devices.
Due to the presence of these computers, the world of computing became more easy and user-friendly. Unlike the first generation of computers which were bulky and big, second generation computers were no longer trapped in massive rooms, in fact they were smaller, and more compact.
In this article we’ll learn what is the second generation of computer, features and characteristics, its advantages and disadvantages, and second generation of computer examples as well. Let’s begin.
What Is The Second Generation Of Computer
A second generation computer is also known as a Transistor computer. The second generation of computer adopted transistors, which are solid-state devices and replaced the heavy and less reliable vacuum tubes used in first-generation computers.
The second generation of computer year was from the late 1950s to the early 1960s. They roughly cover the years 1956 to 1963. The TX-0 was the first computer to use transistors in 1956.
The two important features of the second generation of computer are transistors and magnetic core. The use of transistors made computer systems smaller, which increased their usage in different applications whereas magnetic core memory provided a reliable method of binary data storage.
Additionally, this generation also developed assembly language and early high-level programming, making it easier for developers to interact with computers.
Also Read :
Second Generation Of Computer Examples
As discussed earlier about the second generation of computer year from the late 1950s to early 1960s, there have been various computers developed to be used in different fields. Some of the second generation of computer examples with featured advancements like the use of transistors and magnetic core memory are –
- IBM 7090 (1960) -The IBM 7090, an early second generation of computer examples, was designed for scientific and engineering calculations and featured magnetic core memory.
- UNIVAC 1107 (1962) – It was used for scientific and business applications and was one of the first computers to employ thin-film memory technology.
- CDC 1604 (1960) – known for its high performance in scientific and military applications.
- DEC PDP-1 (1959) – It is one of the second generation of computer examples which was a minicomputer used for various applications, including early computer games.
- IBM 1401 (1959) – Other examples of second generation of computer include IBM 1401 which used transistors and featured a card reader, card punch, and magnetic tape storage.
- Ferranti Mercury (1957) – The Mercury was used for scientific calculations and served as a prototype for later Ferranti computers. It is one of the second generation of computer examples which was developed in the United Kingdom.
- Burroughs B5000 (1961) – It was designed for business and scientific use. This example of second generation of computer featured a stack-based architecture and supported high-level programming languages like ALGOL and COBOL.
Now let’s have a look at the features of the different second generation of computer examples discussed below.
Features Of Second Generation Of Computer
The second generation of computer has several key features that differentiate it from the first generation of computer. Here are some of the features –
Transistors
The most important feature of the second generation of computer was the use of transistors as the primary electronic component. Transistors replaced the vacuum tubes used in first generation computers, leading to a reduction in size, increased reliability, and improved efficiency.
Magnetic Core Memory
Second generation of computer commonly used magnetic core memory for primary storage. This technology used small magnetic cores to store binary data, giving a more reliable and faster option to earlier memory technologies.
Assembly Language and High-Level Programming
The second generation of computer saw the development of assembly language and early high-level programming languages. This made programming really easy, allowing developers to write code that could be read easily by people.
Batch Processing
The second generation of computer was also involved in batch processing, where similar tasks were grouped together and processed one by one. This method also increased efficiency in handling large volumes of data, making computers more practical for business and scientific applications.
Characteristics Of Second Generation Of Computer
There are many unique characteristics of the second generation of computer which have helped developers and common people in many different ways. Such characteristics are –
Smaller In Size
The second generation of computer consisted of much smaller computers than the first generation of computers. It made these computers more practical and accessible.
Durable
Transistors were more durable, had a longer lifespan, and were less open to failures than vacuum tubes.
Easy Maintenance
Second generation of computer was also easier to maintain due to reliable transistors and magnetic core memory and also since they no longer were as big as a room.
Commercial Production
Unlike the first generation, second generation computers were commercially produced and sold by companies, which was an evolution in the computer industry.
Reliable
The use of transistors, magnetic core memory, and assembly language made the second generation of computer more reliable and durable as well which could easily be used by people.
Second Generation Of Computer Images

Advantages Of Second Generation Of Computer
Higher Speed and Performance
Transistors were faster than vacuum tubes, contributing to an overall increase in the speed and performance of the second generation of computer. This improved computational power allowed more complex and difficult calculations.
Lower Power Consumption
Transistors consumed less power than vacuum tubes, resulting in more energy-efficient computers. This was an important factor in making computers more accessible on a large scale.
Commercialization and Business Use
The second generation of computer marked the commercialization of computers, making them available for business and scientific purposes.
Parallel Processing
Some second generation computers were designed with multiple processors, allowing for parallel processing. This approach increased the overall computational capabilities of these machines.
Improved Accuracy
Transistors in the second generation of computer with their higher accuracy, contributed to a reduction in errors and failures compared to the earlier vacuum tube-based systems.
Development of High-Level Programming Languages
Second generation of computer saw the development of high-level programming languages such as COBOL and FORTRAN, which made programming more accessible to a larger audience and increased the development of software applications.
Improved Storage Capacity
In the second generation of computer, magnetic core memory replaced earlier storage methods, providing higher storage capacity and faster access times. This allowed for more great and efficient data handling.
Cost Reduction
The use of transistors, expensive at an early stage to manufacture, eventually led to cost reductions in the production of computers.
Advancements in Operating Systems
The second generation of computer saw the development of more latest operating systems which provided better resource management, task scheduling, and user interaction, making it easier for users to operate and program computers.
Disadvantages Of Second Generation Of Computer
Above we have seen many advantages of second generation of computer and while they represented a significant advancement, they also had certain disadvantages and limitations such as –
Heat Generation
While transistors generated less heat than vacuum tubes, the second generation of computer still produced a considerable amount of heat.
Requirement Of Cooling Systems
Effective cooling mechanisms were necessary to prevent overheating and ensure proper functioning of the systems.
High Cost of Production
High overall cost of manufacturing the second generation of computer limited their accessibility to larger organizations and research institutions.
Maintenance Challenge
Maintenance of second generation computers still required skilled technicians, and troubleshooting and repairing transistor-based systems could be tough.
Limited User-Friendly Interface
Interacting with these second generation of computer typically required a deep understanding of the hardware and the use of low-level programming languages.
Complex Programming
Programming in the second generation of computer involved low-level languages and assembly languages, which could be complex and time-consuming.
Dependence on Batch Processing
Second generation of computer was dependent on batch processing which limited real-time processing capabilities and interactive computing.
Difference Between First And Second Generation Of Computer
The first and second generation of computer represent unique phases in the evolution of computing technology. Here is a list of difference between the first and second generations of computer –
Technology
A main difference between the first and second generations of computer is technology.
- First Generation – First generation computers (1940s to early 1950s) primarily used vacuum tube technology for electronic components.
- Second Generation – The second generation of computer (late 1950s to early 1960s) saw the adoption of transistor technology. Transistors were small, dependable, and produced less heat than vacuum tubes
Size
Another difference between the first and second generations of computer is size.
- First Generation – First generation computers were large and heavy. They often filled entire rooms and required extensive cooling due to the heat generated by vacuum tubes.
- Second Generation – The use of transistors in the second generation of computer significantly reduced their size.
Speed and Performance
- First Generation – First generation computers had limited processing speed and computational power. They were used for basic arithmetic and data processing tasks.
- Second Generation – The adoption of transistors in the second generation of computer increased processing speed and overall performance making them capable of more complex calculations.
Memory Technology
One major difference between the first and second generations of computer is the memory and storage.
- First Generation – First generation computers primarily used punched cards, punched tape, and early magnetic drum storage for memory.
- Second Generation – The second generation of computer introduced magnetic core memory, which provided faster and more reliable storage.
Programming
Programming is also a key difference between the first and second generations of computer.
- First Generation – Programming in the first generation often involved machine language and assembly language.
- Second Generation – Second generation of computer saw the development of higher-level programming languages like COBOL and FORTRAN.
Applications
- First Generation – First generation computers were primarily used for scientific and military applications, such as calculations for defense and scientific research.
- Second Generation – The range of applications expanded in the second generation of computer to include business data processing, and various computational tasks across different industries.
Conclusion
The second generation of computer was a critical period marked by technological advancements. The second generation of computer examples like IBM 7090, UNIVAC 1107, etc. resulted in improved efficiency, reliability, and accessibility of computing technology. This era laid the foundation for the continued evolution of computers into more powerful, versatile, and widely used tools.
Also Read :
- First Generation Of Computer.
- What Is Hybrid Computer ?
- What Is Digital Computer ?
- Difference between Primary and Secondary Memory