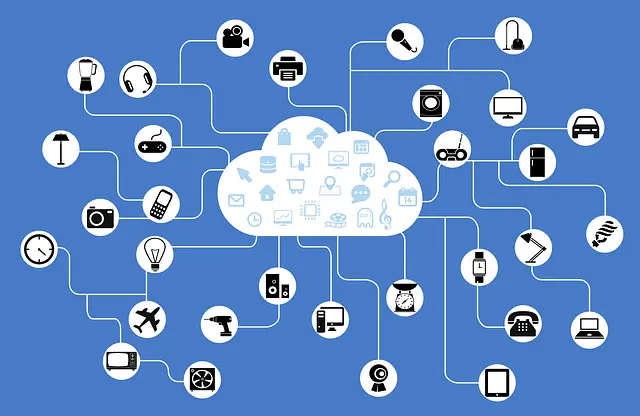
In a world where the lines between the physical and digital field blur, where devices have advanced intelligence and connectivity, a new era has begun. That era is the Internet of Things, a breathtaking combination of innovation and imagination.
The Internet of Things (IoT) refers to the network of physical devices, vehicles, appliances and other objects inserted with sensors, software and connectivity which allows them to collect and exchange data over the internet. These devices, often referred to as smart or connected devices, can communicate with each other and with humans, allowing for remote monitoring, control and mechanization of various processes.
Internet Of Things History
The term Internet of Things was coined by Kevin Ashton, a British entrepreneur. The planning for IoT is placed with the development of RFID technology and the integration of sensors into various devices. Earlier IoT was used for only supply chain management and industrial practices.
However, the emergence of wireless technologies such as Wi-Fi and Bluetooth enabled the expansion of connected devices. Later in 2008 the number of connected devices surpassed the number of people on the planet, marking a significant milestone in the growth of IoT.
The IoT gained popularity in various industries including smart homes, healthcare, agriculture, transportation and industrial automation. Advancements in cloud computing, big data analytics and artificial intelligence also supported the growth of IoT applications.
Now the IoT continues to expand, improved edge computing technologies, 5G connectivity and the increment of IoT platforms. Smart cities, autonomous vehicles and wearables are among the areas witnessing significant IoT advancements.
Mechanism Of Internet Of Things
The IoT functions by combining physical devices equipped with sensors with digital networks. These devices collect data from their environment through sensors such as temperature, motion or light sensors. The collected data is then transmitted through various connectivity options, including Wi-Fi, Bluetooth or cellular networks, to cloud-based servers or local gateways for processing.
Once the data reaches the cloud or gateway, it undergoes processing and analysis to extract valuable information. This involves filtering, aggregating and transforming the raw data into meaningful information.
For smooth communication between devices, IoT systems employ various communication arrangements such as MQTT, CoAP or HTTP which ensure efficient transmission of data. The processed data is then stored in databases.
Advanced analytics techniques, including machine learning and artificial intelligence can be applied to discover patterns, detect anomalies and make predictions based on the collected data.
Applications Of IoT
The IoT has a wide range of applications across various industries and domains such as :
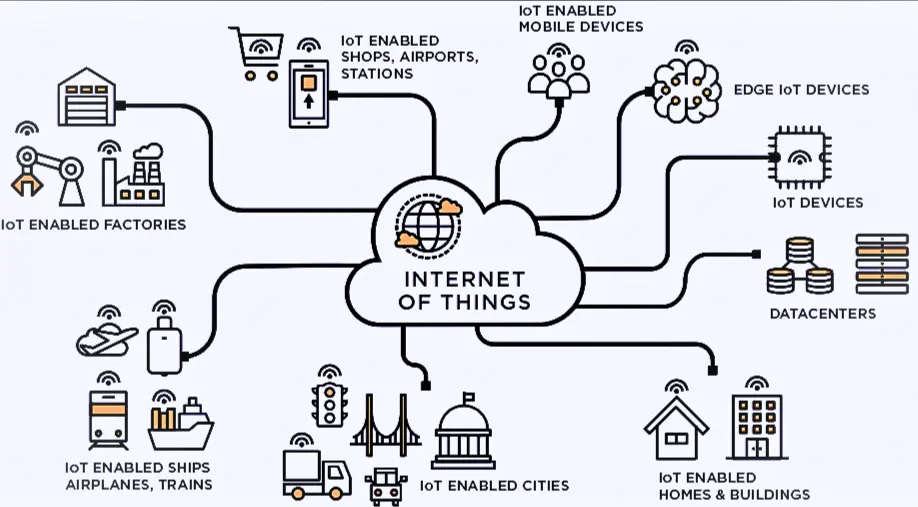
Smart Homes
IoT makes it possible to build smart homes with connected and remote-controllable appliances, lighting, security, and thermostat systems. Homeowners can take control of their indoor environment, improve convenience and security, and use energy more effectively.
Healthcare
IoT has many uses in the healthcare industry, including technology, medical equipment and remote patient monitoring. Vital sign monitoring, real-time health data, are all made possible by IoT enabled healthcare systems, resulting in more individualized and effective patient care.
Smart Cities
Smart and sustainable cities are largely made possible by IoT. Cities may monitor and control a variety of factors, including traffic flow, parking, trash management, energy usage and environmental conditions, by integrating sensors, networks, and data analytics.
Agriculture
Smart agricultural practices are made possible by IoT technology, which is transforming the agricultural industry. IoT-based solutions aid in tracking livestock, managing crop development, and monitoring soil conditions, which leads to increased agricultural yields, less resource waste, and sustainable farming practices.
Transportation And Logistics
Through tools like supply chain optimization, fleet management and asset tracking, IoT is expanding the logistics and transportation sector. Connected sensors and devices offer real-time visibility into the location, state, and movement of items, resulting in increased efficiency, lower costs, and more customer satisfaction.
Why Is IoT Important
IoT is revolutionary with profound implications. It enables connectivity, automation and data exchange, transforming industries and daily life. IoT enhances efficiency, user experiences, safety, decision making, and economic growth. It creates a web of interconnected devices, optimizing processes and unlocking new opportunities. Hybrid technology is frequently incorporated into IoT networks to send data for monitoring and control.
However, privacy, security, and interoperability challenges must be carefully addressed. Harnessing IoT’s potential requires robust measures to protect data and ensure seamless integration. The future holds limitless possibilities as IoT continues to reshape our world. Embracing its transformative power will lead us to a more connected, efficient, and prosperous future.
Conclusion
In conclusion, IoT represents an innovative technological shift that has the potential to reshape industries, enhance our daily lives and drive economic growth. It offers a range of benefits, including improved user experiences, enhanced safety, optimized resource utilization and informed decision making.
FAQs
what does the internet of things (iot) enable?
It enables the connection of physical devices equipped with sensors with digital networks.
how does 5g technology enhance the internet of things (iot)?
5g technology enhance the Iot by increasing faster data transfer speed with lower latency.